Embark on a scientific expedition with AP Biology Diffusion and Osmosis Lab Answers, where we delve into the fundamental processes that govern the movement of molecules across biological membranes. Diffusion and osmosis, the driving forces behind cellular transport, play a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis and facilitating vital life functions.
Our comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of these concepts, equipping you with the knowledge and insights to excel in your AP Biology studies and beyond.
Introduction: Ap Biology Diffusion And Osmosis Lab Answers

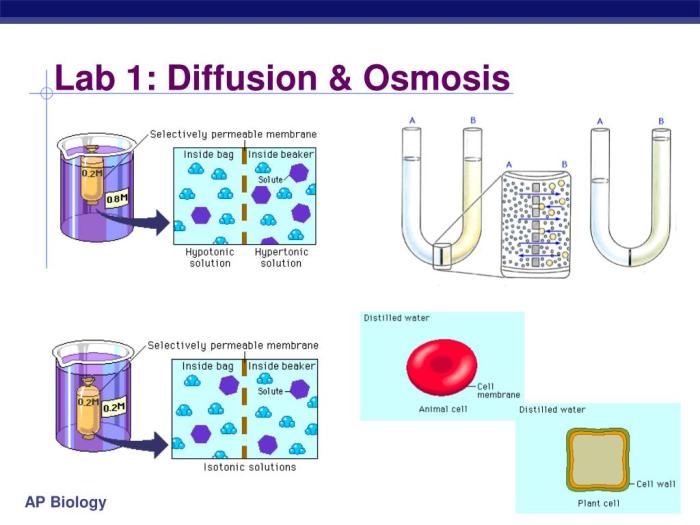
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental processes that occur in all living organisms. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
These processes are essential for the survival of cells and organisms. Diffusion allows cells to take in nutrients and expel waste products, while osmosis helps to maintain the proper water balance of cells.
Materials, Ap biology diffusion and osmosis lab answers
- Diffusion tubes
- Semipermeable membranes
- Solutions of different concentrations
- Stopwatch
- Ruler
Methods
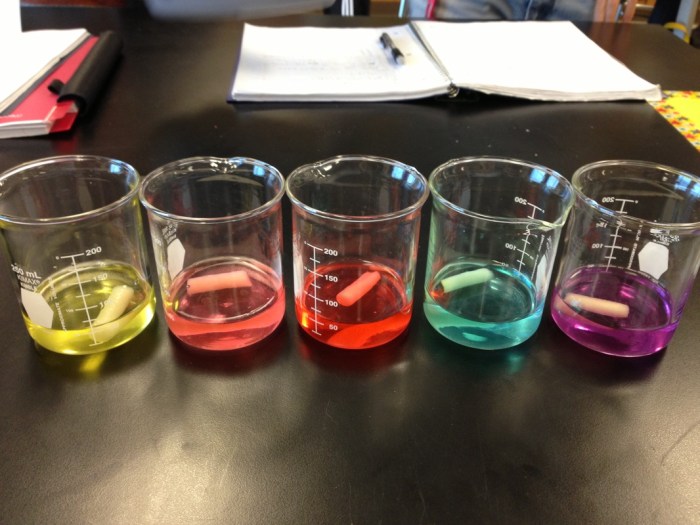
- Set up the diffusion tubes by filling one end with a solution of high concentration and the other end with a solution of low concentration. The semipermeable membrane should be placed in the middle of the tube.
- Start the stopwatch and observe the movement of the molecules across the membrane.
- Record the distance that the molecules travel over time.
- Repeat the experiment with different concentrations of solutions.
Results
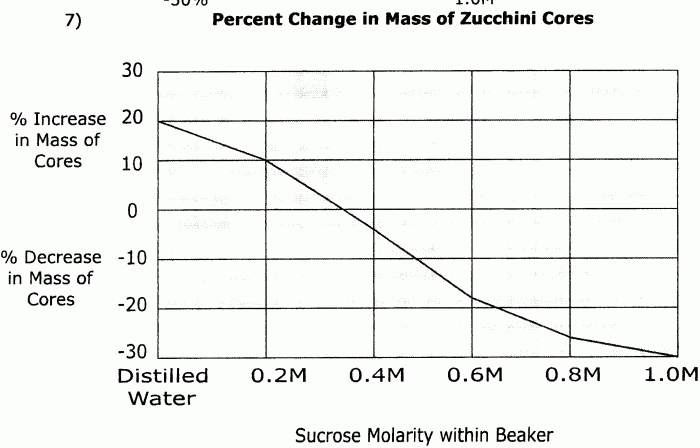
The results of the experiment will show that the rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration gradient. This means that the greater the difference in concentration between the two solutions, the faster the rate of diffusion.
The results will also show that the rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the thickness of the membrane. This means that the thicker the membrane, the slower the rate of diffusion.
Discussion
The results of this experiment support the theory of diffusion. They show that the rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration gradient and inversely proportional to the thickness of the membrane.
These findings have important implications for the functioning of cells. They help to explain how cells are able to take in nutrients and expel waste products, and how they are able to maintain the proper water balance.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion and osmosis?
Temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, and membrane permeability all influence the rate of diffusion and osmosis.