Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of atoms and isotopes, unraveling their fundamental concepts and practical applications. This comprehensive guide to atoms and isotopes worksheet answers will illuminate the intricate world of these building blocks of matter, empowering you with a deeper understanding of their properties, behaviors, and significance in various scientific disciplines.
Delving into the depths of this worksheet, you will explore the defining characteristics of atoms, decipher the mysteries of atomic number and mass number, and delve into the captivating realm of isotopes. Prepare to unravel the distinctions between these atomic variations, unlocking the secrets of their unique properties and applications.
Basic Concepts of Atoms and Isotopes: Atoms And Isotopes Worksheet Answers
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. They are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus.
The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus, which determines the element to which it belongs. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, which determines the isotope of the element.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Worksheet Analysis
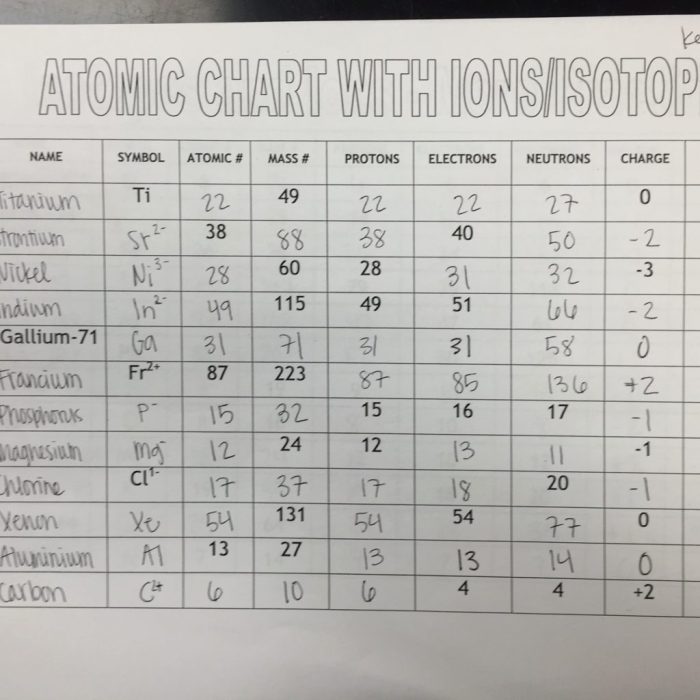
The given worksheet on atoms and isotopes aims to assess students’ understanding of the basic concepts of atoms, isotopes, and their properties. It covers key topics such as atomic structure, isotope notation, and applications of isotopes.
The worksheet provides exercises and questions that require students to apply their knowledge to solve problems and demonstrate their comprehension of the subject matter.
Types of Isotopes, Atoms and isotopes worksheet answers
There are three main types of isotopes: stable, radioactive, and synthetic.
- Stable isotopesdo not undergo radioactive decay and are found naturally in the environment.
- Radioactive isotopesundergo radioactive decay, emitting particles or energy to transform into a different element.
- Synthetic isotopesare created artificially through nuclear reactions.
Radioactive Isotopes
Radioactive isotopes have unstable nuclei and decay over time, emitting radiation. The rate of decay is characterized by the isotope’s half-life, which is the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay.
Radioactive isotopes have numerous applications in fields such as medicine, energy production, and environmental science.
Isotope Notation
Isotopes can be represented using different notation methods:
- Mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, written as a superscript before the element symbol (e.g., 12C).
- Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus, written as a subscript before the element symbol (e.g., 6C).
- Element symbol: The chemical symbol of the element, followed by a hyphen and the mass number (e.g., C-12).
Applications of Atoms and Isotopes
Atoms and isotopes have a wide range of applications in various fields:
- Medicine: Diagnostic imaging, cancer treatment, sterilization of medical equipment
- Energy production: Nuclear power plants, isotope dating
- Environmental science: Tracing pollutants, dating fossils, studying climate change
Q&A
What is the difference between an atom and an isotope?
An atom is the fundamental unit of matter, composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Isotopes are variations of the same element that share the same atomic number but differ in their neutron count, resulting in different mass numbers.
What are the three main types of isotopes?
Isotopes are classified into three primary types: stable isotopes, radioactive isotopes, and synthetic isotopes. Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay, while radioactive isotopes emit radiation and decay over time. Synthetic isotopes are created artificially in laboratory settings.
What are the applications of radioactive isotopes?
Radioactive isotopes have a wide range of applications, including medical imaging and treatment, energy production in nuclear power plants, and tracing pollutants in environmental science.