Is GPA discrete or continuous? This question sets the stage for an intriguing exploration into the nature of Grade Point Average (GPA). As we delve into the characteristics of GPA, we’ll uncover its unique properties and examine the arguments for classifying it as either a discrete or continuous variable.
Throughout this discussion, we’ll unravel the implications of considering GPA as discrete versus continuous, shedding light on how it influences data analysis, interpretation, and decision-making.
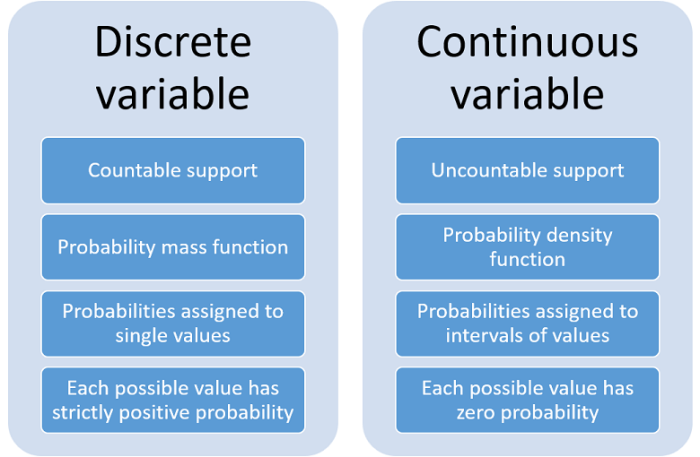
Definition of Discrete and Continuous Variables
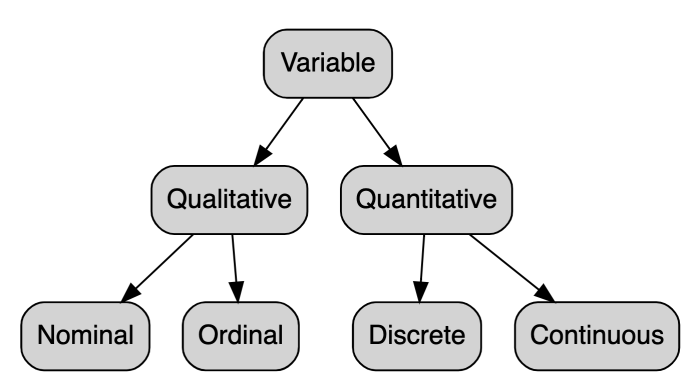
Variables are classified into two main types: discrete and continuous. The distinction between these two types lies in the nature of the values they can take.
A discrete variableis one that can take on only certain distinct values. For example, the number of students in a class is a discrete variable because it can only take on whole number values (1, 2, 3, …). Other examples of discrete variables include the number of heads when flipping a coin, the number of people in a household, and the number of days in a month.
A continuous variable, on the other hand, is one that can take on any value within a given range. For example, the height of a person is a continuous variable because it can take on any value between a certain minimum and maximum (e.g.,
between 4 feet and 7 feet).
Nature of GPA: Is Gpa Discrete Or Continuous
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a numerical representation of a student’s academic performance over a period of time, typically a semester or a year. It is calculated by taking the average of all the grades earned in a set of courses, weighted by the number of credits assigned to each course.
Characteristics of GPA
GPA has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other types of variables:
- Numeric:GPA is a numeric value, typically ranging from 0.0 to 4.0 or 5.0.
- Interval:GPA is measured on an interval scale, meaning that the differences between the values are meaningful. For example, a GPA of 3.0 is higher than a GPA of 2.0, and the difference between the two is 1.0.
- Non-negative:GPA cannot be negative, as it is calculated by averaging grades that are typically non-negative.
Is GPA Discrete or Continuous?
The question of whether GPA is discrete or continuous is a matter of debate. Some argue that GPA is discrete because it is calculated using a finite number of grades, each of which is assigned a specific value. Others argue that GPA is continuous because it can take on any value within a certain range, and that the differences between the values are meaningful.
Ultimately, the classification of GPA as discrete or continuous depends on the specific context in which it is being used. For example, if GPA is being used to determine eligibility for a scholarship, it may be treated as a discrete variable, as it is typically rounded to the nearest whole number.
However, if GPA is being used to predict a student’s future academic success, it may be treated as a continuous variable, as it can take on any value within a certain range.
Arguments for Discrete GPA
GPA can be considered a discrete variable because it is typically reported as a whole number or a fraction with a limited number of decimal places. This is in contrast to continuous variables, which can take on any value within a specified range.
Examples
- A student’s GPA is reported as 3.5.
- A student’s GPA is reported as 2/3.
- A student’s GPA is reported as 4.0.
In each of these cases, the GPA is a discrete value that can only take on a limited number of possible values.
Arguments for Continuous GPA
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a measure of academic performance that is often used to assess students’ progress and achievement. Traditionally, GPA has been treated as a discrete variable, meaning it can only take on specific, whole-number values (e.g.,
3.0, 3.5, 4.0). However, some researchers argue that GPA should be considered a continuous variable, meaning it can take on any value within a given range (e.g., 3.25, 3.78, 3.99).
There are several reasons why GPA could be considered a continuous variable. First, GPA is calculated by averaging the grades earned in a set of courses. Since grades are typically assigned on a continuous scale (e.g., 0-100%), the average of these grades will also be continuous.
Second, GPA is often used to make decisions about students’ future, such as college admission or scholarship eligibility. These decisions are typically based on a student’s overall academic performance, which is best represented by a continuous measure like GPA.
Whether GPA is discrete or continuous has been a subject of debate among statisticians. Some argue that it is discrete because it can only take on certain values, such as whole numbers or tenths of a number. Others contend that it is continuous because it can take on any value within a certain range.
To learn more about this topic and other related topics, check out the ap human geography unit 3 frq for further insights.
Examples of Continuous GPA, Is gpa discrete or continuous
- A student who earns an A in one course and a B in another course has a GPA of 3.5.
- A student who earns an A+ in one course, a B+ in another course, and a C+ in a third course has a GPA of 3.67.
- A student who earns an A in all of their courses has a GPA of 4.0.
These examples illustrate that GPA can take on any value within a given range, which is a characteristic of a continuous variable.
Implications of Discrete vs. Continuous GPA
The choice between considering GPA as discrete or continuous has significant implications for data analysis, interpretation, and decision-making.
Data Analysis
- Discrete GPA: Statistical analysis methods suitable for discrete data must be employed, such as frequency distributions, chi-square tests, and non-parametric tests.
- Continuous GPA: A wider range of statistical analysis methods can be used, including parametric tests, regression analysis, and ANOVA.
Interpretation
- Discrete GPA: Interpretation is straightforward, as each value represents a distinct grade point.
- Continuous GPA: Interpretation can be more nuanced, as values may fall within a range of grade points.
Decision-Making
- Discrete GPA: Decisions based on GPA may be more clear-cut, as students with higher GPAs will have a distinct advantage.
- Continuous GPA: Decisions may be more nuanced, as students with similar GPAs may have slightly different grade point averages.
FAQs
Is GPA a whole number?
GPA is typically not a whole number as it can take on fractional values, such as 3.5 or 4.2.
Can GPA be negative?
GPA is typically non-negative, as it represents academic achievement and cannot be less than zero.